Windows Subsystem for Linux
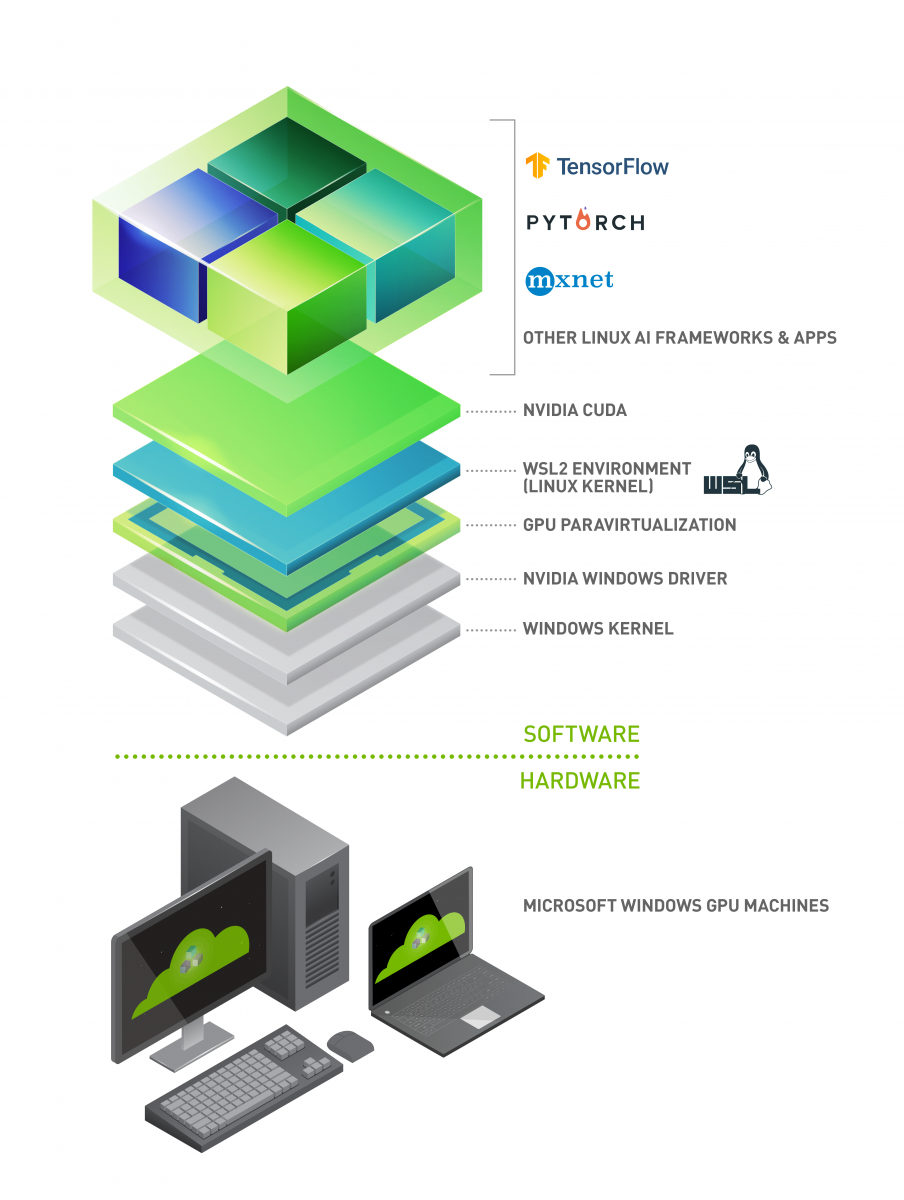
If you want to train deep learning models under Windows in a Linux environment you can use the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL2). The advantage of WSL2 about a virtual machine is that it can use the installed graphics drivers for your NVIDIA GPU, so you don't have to install new drivers in the Linux environment.
Microsoft offers a nice tutorial for seetting up WSL2 on your device here: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install
You should then go to the Microsoft Store app on your PC and download the Ubuntu WSL2 package. After the installation the Ubuntu terminal is available in Windows' terminal app.
Check if NVIDIA GPU is available
You can check if the Ubuntu environment can see the GPU using the following command:
nvidia-smi
You don't need to install any drivers becausue the WSL environments share the drivers with the Windows operating system. What needs to be installed is CUDA. We show you how you can do this and how you can use different CUDA versions per project using Conda.
Here is a nice article how GPU virtualization with WSL works:
https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda/wsl
Install CUDA using Conda
You can install CUDA versions using the Conda package manager. Nvidia has an article about how you can do this here:
https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-installation-guide-linux/index.html#installing-cuda-using-conda
The available CUDA packages can be found here:
Available CUDA packages: https://anaconda.org/nvidia/cuda/labels
For installing a specific CUDA version in your Conda environment just run on of these commands:
# CUDA 11.8
$ conda install cuda -c nvidia/label/cuda-11.8.0
# CUDA 12.4
$ conda install cuda -c nvidia/label/cuda-12.4.0
Sometimes executing Python code doesn't work after installing CUDA. You will get the following error message:
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named '_sysconfigdata_x86_64_conda_cos7_linux_gnu'
The solution is to close the terminal and reopen it again.